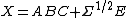- Definition
- History
- Applications
- Other uses
- Footnotes
- References
The growth curve model in statistics is a specific multivariate linear model, also known as GMANOVA (Generalized Multivariate ANalysis-Of-VAriance).[1] It generalizes MANOVA by allowing post-matrices, as seen in the definition.
Definition
Growth curve model:[2] Let X be a p×n random matrix corresponding to the observations, A a p×q within design matrix with q ≤ p, B a q×k parameter matrix, C a k×n between individual design matrix with rank(C) + p ≤ n and let Σ be a positive-definite p×p matrix. Then
defines the growth curve model, where A and C are known, B and Σ are unknown, and E is a random matrix distributed as Np,n(0,Ip,n).
This differs from standard MANOVA by the addition of C, a "postmatrix".[3]
History
Many writers have considered the growth curve analysis, among them Wishart (1938),[3] Box (1950) [4] and Rao (1958).[5] Potthoff and Roy in 1964;[6] were the first in analyzing longitudinal data applying GMANOVA models.
Applications
GMANOVA is frequently used for the analysis of surveys, clinical trials, and agricultural data,[7] as well as more recently in the context of Radar adaptive detection.[8][9]
Other uses
In mathematical statistics, growth curves such as those used in biology are often modeled as being continuous stochastic processes, e.g. as being sample paths that almost surely solve stochastic differential equations.[10] Growth curves have been also applied in forecasting market development.[11]
Footnotes
2. ^{{cite book|author1=Kollo, Tõnu |author2=von Rosen, Dietrich|chapter="Multivariate linear models" (chapter 4), especially "The Growth curve model and extensions" (Chapter 4.1)|title=Advanced multivariate statistics with matrices|series=Mathematics and its applications|location=Dordrecht|volume=579|publisher=Springer|year=2005|isbn=978-1-4020-3418-3}}
3. ^{{Cite journal|last=Wishart|first=John|year=1938|title=Growth rate determinations in nutrition studies with the bacon pig, and their analysis|url=|journal=Biometrika|volume=30|pages=16–28|via=|doi=10.1093/biomet/30.1-2.16}}
4. ^{{Cite journal|last=Box|first=G.E.P.|year=1950|title=Problems in the analysis of growth and wear curves|url=|journal=Biometrics|volume=6|pages=362–89|via=|doi=10.2307/3001781}}
5. ^{{Cite journal|last=Radhakrishna|first=Rao|year=1958|title=Some statistical methods for comparison of growth curves.|url=|journal=Biometrics|volume=14|pages=1–17|via=|doi=10.2307/2527726}}
6. ^1 R.F. Potthoff and S.N. Roy, “A generalized multivariate analysis of variance model useful especially for growth curve problems,”Biometrika, vol. 51, pp. 313–326, 1964
7. ^{{cite book|author1=Pan, Jian-Xin |author2=Fang, Kai-Tai|title=Growth curve models and statistical diagnostics|series=Springer Series in Statistics|publisher=Springer-Verlag|location=New York|year=2002|isbn=0-387-95053-2}}
8. ^{{cite journal|last1 = Ciuonzo|first1 = D.|last2 = De Maio|first2 = A.|last3 = Orlando|first3 = D.|title = A Unifying Framework for Adaptive Radar Detection in Homogeneous plus Structured Interference-Part I: On the Maximal Invariant Statistic|journal = IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing|date = 2016|volume = PP|issue = 99|pages = 1-1|doi = 10.1109/TSP.2016.2519003|arxiv = 1507.05263|bibcode = 2016ITSP...64.2894C}}
9. ^{{cite journal|last1 = Ciuonzo|first1 = D.|last2 = De Maio|first2 = A.|last3 = Orlando|first3 = D.|title = A Unifying Framework for Adaptive Radar Detection in Homogeneous plus Structured Interference-Part II: Detectors Design|journal = IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing|date = 2016|volume = PP|issue = 99|pages = 1-1|doi = 10.1109/TSP.2016.2519005|arxiv = 1507.05266|bibcode = 2016ITSP...64.2907C}}
10. ^{{cite book|author1=Seber, G. A. F. |author2=Wild, C. J.|chapter="Growth models (Chapter 7)"|pages=325–367|title=Nonlinear regression|series=Wiley Series in Probability and Mathematical Statistics: Probability and Mathematical Statistics|publisher=John Wiley & Sons, Inc.|location=New York|year=1989|isbn=0-471-61760-1}}
11. ^{{Cite journal|last=Meade|first=Nigel|year=1984|title=The use of growth curves in forecasting market development—a review and appraisal|url=|journal=Journal of Forecasting|volume=3|pages=429–451|via=|doi=10.1002/for.3980030406}}
References
- {{cite book
|title=Nonlinear Models for Repeated Measurement Data
|first=Marie
|last=Davidian | authorlink = Marie Davidian
|author2=David M. Giltinan
|series=Chapman & Hall/CRC Monographs on Statistics & Applied Probability
|isbn=978-0-412-98341-2
|year=1995
}}
- {{cite book
|author1=Kshirsagar, Anant M. |author2=Smith, William Boyce
|title=Growth curves
|series=Statistics: Textbooks and Monographs
|volume=145
|publisher=Marcel Dekker, Inc.
|location=New York
|year=1995
|isbn=0-8247-9341-2
}}
- {{cite book
|last=Pan
|first=Jianxin
|author2=Fang, Kaitai
|title=Growth curve models and statistical diagnostics
|series=Mathematical Monograph Series
|volume=8
|publisher=Science Press
|location=Beijing
|year=2007
|isbn=9780387950532
}}
- {{cite book
|author=Timm, Neil H.
|chapter="The general MANOVA model (GMANOVA)" (Chapter 3.6.d)
|title=Applied multivariate analysis
|series=Springer Texts in Statistics
|publisher=Springer-Verlag
|location=New York
|year=2002
|isbn=0-387-95347-7
}}
- {{cite book |author1=Vonesh, Edward F. |author2=Chinchilli, Vernon G. | title = Linear and Nonlinear Models for the Analysis of Repeated Measurements| publisher = London: Chapman and Hall | year = 1997
}}{{Least Squares and Regression Analysis}}
- Gert Gunther Hoffmann
- Gert Günther Hoffmann
- Gerth
- Gert Haucke
- Gert Heerkes
- Gert Hildebrand
- Gerth Stølting Brodal
- Gertia
- Gerti Bogdani
- Gerti Daub
- Gerti Daub Hollman
- Gerti Daub Hollmann
- Gerti Deutsch
- Gertie Eggink
- Gertie Gets Her Ducks in a Row
- Gertie on Tour
- Gertie the Duck (Gillen)
- Gertie the Duck Statue
- Gertigh
- Gert-Inge Sigfridsson
- Gertin Hoxhalli
- Gerti Shima
- Gert Jakobs
- Gert-Jan Cieremans
- Gert Jan Droge