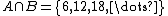- Uniqueness
- Intersection of two sets
- Examples in classical geometry
- Notation
- See also
- References
In mathematics, the intersection of two or more objects is another, usually "smaller" object. All objects are presumed to lie in a certain common space except in set theory, where the intersection of arbitrary sets is defined. The intersection is one of basic concepts of geometry. Intuitively, the intersection of two or more objects is a new object that lies in each of original objects. An intersection can have various geometric shapes, but a point is the most common in a plane geometry.
Definitions vary in different contexts: set theory formalizes the idea that a smaller object lies in a larger object with inclusion, and the intersection of sets is formed of elements that belong to all intersecting sets. It is always defined, but may be empty. Incidence geometry defines an intersection (usually, of flats) as an object of lower dimension that is incident to each of original objects. In this approach an intersection can be sometimes undefined, such as for parallel lines. In both cases the concept of intersection relies on logical conjunction.
Algebraic geometry defines intersections in its own way with intersection theory.
Uniqueness
There can be more than one primitive object, such as points (pictured above), that form an intersection. The intersection can be viewed collectively as all of the shared objects (i.e., the intersection operation results in a set, possibly empty), or as several intersection objects (possibly zero).
Intersection of two sets
{{Main|Intersection (set theory)}}The intersection of two sets A and B is the set of elements which are in both A and B. In symbols,
.[1]
For example, if A = {1, 3, 5, 7} and B = {1, 2, 4, 6} then A ∩ B = {1}. A more elaborate example (involving infinite sets) is:
A = {x is an even integer}
B = {x is an integer divisible by 3}
As another example, the number 9 is not contained in the intersection of the set of prime numbers {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, …} and the set of even numbers {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, …}, because 9 is neither prime nor even.
Examples in classical geometry
{{further|Intersection (Euclidean geometry)}}- Line–line intersection
- Line–plane intersection
- Line–sphere intersection
- Intersection of a polyhedron with a line
- Line segment intersection
- Intersection curve
Notation
Intersection is denoted by the {{unichar|2229|intersection}} from Unicode Mathematical Operators.
{{expand section|history of the symbol|date=January 2014}}See also
- Constructive solid geometry, Boolean Intersection is one of the ways of combining 2D/3D shapes
- Meet (lattice theory)
References
- Keep On Smilin' (John Paul Young song)
- Keep On The Sunny Side: June Carter Cash - Her Life In Music
- Keep on the Sunny Side: June Carter Cash - Her Life In Music
- Keep on the Sunny Side: June Carter Cash – Her Life in Music
- Keep on Training: Pop Goes the Water Ballon!
- Keep on Training: Pop Goes the Water Balloon!
- Keep on Truckin'
- Keep On Truckin'
- Keep on truckin'
- Keep on Truckin' (comics)
- Keep on Truckin' (disambiguation)
- Keep on Truckin' (Family Guy)
- Keep on Trucking
- Keep on Truckin' (song)
- Keep on Walking (CD)
- Keep on Your Mean Side
- Keep On Your Mean Side
- Keep out
- Keep Passing the Open Windows
- Keep Pushin' On
- Keep Reachin Up
- Keeps
- Keepsake
- Keepsake (band)
- Keepsake (Barbershop quartet)