- History
- See also
- References
- External links
The Schauder fixed point theorem is an extension of the Brouwer fixed point theorem to topological vector spaces, which may be of infinite dimension. It asserts that if  is a nonempty convex closed subset of a Hausdorff topological vector space
is a nonempty convex closed subset of a Hausdorff topological vector space  and
and 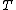 is a continuous mapping of
is a continuous mapping of  into itself such that
into itself such that 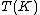 is contained in a compact subset of
is contained in a compact subset of  , then
, then 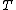 has a fixed point.
has a fixed point.
A consequence, called Schaefer's fixed point theorem, is particularly useful for proving existence of solutions to nonlinear partial differential equations.
Schaefer's theorem is in fact a special case of the far reaching Leray–Schauder theorem which was discovered earlier by Juliusz Schauder and Jean Leray.
The statement is as follows:
Let 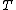 be a continuous and compact mapping of a Banach space
be a continuous and compact mapping of a Banach space 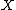 into itself, such that the set
into itself, such that the set
is bounded. Then 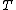 has a fixed point.
has a fixed point.
History
The theorem was conjectured and proven for special cases, such as Banach spaces, by Juliusz Schauder in 1930. His conjecture for the general case was published in the Scottish book. In 1934, Tychonoff proved the theorem for the case when K is a compact convex subset of a locally convex space. This version is known as the Schauder–Tychonoff fixed point theorem. B. V. Singbal proved the theorem for the more general case where K may be non-compact; the proof can be found in the appendix of Bonsall's book (see references).
See also
- Fixed-point theorems
- Banach fixed-point theorem
- Kakutani fixed-point theorem
References
- J. Schauder, Der Fixpunktsatz in Funktionalräumen, Studia Math. 2 (1930), 171–180
- A. Tychonoff, Ein Fixpunktsatz, Mathematische Annalen 111 (1935), 767–776
- F. F. Bonsall, Lectures on some fixed point theorems of functional analysis, Bombay 1962
- D. Gilbarg, N. Trudinger, Elliptic Partial Differential Equations of Second Order. {{ISBN|3-540-41160-7}}.
- E. Zeidler, Nonlinear Functional Analysis and its Applications, I - Fixed-Point Theorems
External links
- {{springer|title=Schauder theorem|id=p/s083320}}
- {{planetmath reference|title=Schauder fixed point theorem|id=4455}} with attached proof (for the Banach space case).
- Arthur Teixeira
- Arthur T. Emerson
- Arthur Temple
- Arthur Temple Lytlleton
- Arthur Temple Lyttelton
- Arthur Tenney Emerson
- Arthur TF Reynolds
- Arthur Thomas (disambiguation)
- Arthur Thomas (Emmerdale)
- Arthur Thomas (Glamorgan cricketer)
- Arthur Thomas Ippen
- Arthur Thomas Lloyd
- Arthur Thomas (rugby league)
- Arthur Thomas Thrupp
- Arthur Thompson
- Arthur Thompson (disambiguation)
- Arthur Thompson (English footballer)
- Arthur Thomson
- Arthur Thomson (anatomist)
- Arthur Thomson (disambiguation)
- Arthur Thomson (footballer)
- Arthur Thomson (footballer, born 1903)
- Arthur Thomson (footballer, born 1948)
- Arthur Thomson (physician)
- Arthur Thornhill