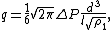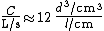- Cylindrical tube
- References
In fluid dynamics, the Knudsen equation is used to describe how gas flows through a tube in free molecular flow. When the mean free path of the molecules in the gas is larger than or equal to the diameter of the tube, the molecules will interact more often with the walls of the tube than with each other. For typical tube dimensions, this occurs only in high or ultrahigh vacuum.
The equation was developed by Martin Hans Christian Knudsen (1871–1949), a Danish physicist who taught and conducted research at the Technical University of Denmark.
Cylindrical tube
For a cylindrical tube, the Knudsen equation is:[1]
where:
| Quantity | Description |
|---|---|
| q | volume flow rate at unit pressure (volume×pressure/time) |
| ΔP | pressure drop from the beginning of the tube to the end |
| d | diameter of the tube |
| l | length of the tube |
| ρ1 | ratio of density and pressure |
For nitrogen (or air) at room temperature, the conductivity  (in liters per second) of a tube can be calculated from this equation:[2]
(in liters per second) of a tube can be calculated from this equation:[2]
References
2. ^{{Citation| publisher = Leybold| last = Umrath| first = Walter| title = Fundamentals of vacuum technology; Leybold Vacuum Products and Reference Book 2001/2002| year = 2001| origyear = 1998| page = 14}}
- Kid (rapper)
- Kid Rhino
- Kidrobot
- Kid robot
- Kid Robot
- Kid rock
- Kid Rock discography
- Kidron
- Kidron ohio
- Kidron, Ohio
- .kids
- Kids (1970s magazine)
- Kids (2000s magazine)
- Kidsafe
- Kids Against Combs
- Kids Against Hunger
- Kids Alive
- Kids are alright (song)
- Kids Are United
- Kids Are United EP
- Kidsbeat
- Kids Books
- KidsCan
- Kids Can Rock and Roll
- KidsCare