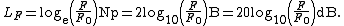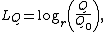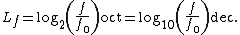- Power level{{anchor|Power quantities}}
- Field (or root-power) level{{anchor|Root-power quantities|Field quantities}}
- Standards
- Related quantities Logarithmic ratio quantity Frequency level
- See also
- Notes
- References
In science and engineering, a power level and a field level (also called a root-power level) are logarithmic measures of certain quantities referenced to a standard reference value of the same type.
- A power level is a logarithmic quantity used to measure power, power density or sometimes energy, with commonly used unit decibel (dB).
- A field level (or root-power level) is a logarithmic quantity used to measure quantities of which the square is typically proportional to power, etc., with commonly used units neper (Np) or decibel (dB).
The type of level and choice of units indicate the scaling of the logarithm of the ratio between the quantity and it reference value, though a logarithm may be considered to be a dimensionless quantity.{{sfn|IEEE/ASTM SI 10|2016|pp=26–27}}{{sfn|ISO 80000-3|2006}}{{sfn|Carey|2006|pp=61–75}} The reference values for each type of quantity are often specified by international standards.
Power and field levels are used in electronic engineering, telecommunications, acoustics and related disciplines. Power levels are used for signal power, noise power, sound power, sound exposure, etc. Field levels are used for voltage, current, sound pressure.{{sfn|ISO 80000-8|2007}}{{clarify|date=February 2019}}
Power level{{anchor|Power quantities}}
Level of a power quantity, denoted LP, is defined by
where
- P is the power quantity;
- P0 is the reference value of P.
Field (or root-power) level{{anchor|Root-power quantities|Field quantities}}
The level of a root-power quantity (also known as a field quantity), denoted LF, is defined by{{sfn|D'Amore|2015}}
where
- F is the root-power quantity, proportional to the square root of power quantity;
- F0 is the reference value of F.
If the power quantity P is proportional to F2, and if the reference value of the power quantity, P0, is in the same proportion to F02, the levels LF and LP are equal.
The neper, bel, and decibel (one tenth of a bel) are units of level that are often applied to such quantities as power, intensity, or gain.{{sfn|Taylor|1995}} The neper, bel, and decibel are related by
- {{nowrap|1=1 B = {{sfrac|1|2}} loge10 Np}};
- {{nowrap|1=1 dB = 0.1 B = {{sfrac|1|20}} loge10 Np}}.
Standards
Level and its units are defined in ISO 80000-3.
The ISO standard defines each of the quantities power level and field level to be dimensionless, with {{nowrap|1=1 Np = 1}}. This is motivated by simplifying the expressions involved, as in systems of natural units.
Related quantities
Logarithmic ratio quantity
Power and field quantities are part of a larger class, logarithmic ratio quantities.
ANSI/ASA S1.1-2013 defines a class of quantities it calls levels. It defines a level of a quantity Q, denoted LQ, as{{sfn|ANSI/ASA S1.1|2013|loc=entry 3.01}}
where
- r is the base of the logarithm;
- Q is the quantity;
- Q0 is the reference value of Q.
For the level of a root-power quantity, the base of the logarithm is {{nowrap|1=r = e}}.
For the level of a power quantity, the base of the logarithm is {{nowrap|1=r = e2}}.{{sfn|Ainslie|2015}}
Frequency level
Frequency level of a frequency f is the logarithm of a ratio of the frequency f to a reference frequency f{{sub|0}}. The reference frequency is C{{sub|0}}, four octaves below middle C. {{sfn|ANSI/ASA S1.1|2013}}
In electronics, the octave (oct) is used as a unit with logarithm base 2, and the decade (dec) is used as a unit with logarithm base 10:
In music theory, the octave is a unit used with logarithm base 2 (called interval).{{sfn|Fletcher|1934|pp=59–69}} A semitone is one twelfth of an octave. A cent is one hundredth of a semitone.
See also
- {{section link|Decibel|Definition}}
- Field, power, and root-power quantities
- Logarithmic scale
- Sound level (disambiguation)
- Leveling (tapered floating point)
- Level-index arithmetic (LI) and symmetric level-index arithmetic (SLI)
Notes
References
- {{citation |year=1934 |author=Fletcher |first=H |title=Loudness, pitch and the timbre of musical tones and their relation to the intensity, the frequency and the overtone structure |journal=Journal of the Acoustical Society of America |volume=6 |issue=2 }}
- {{citation |year=1995 |author=Taylor |first=Barry |title=Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI): The Metric System |publisher=Diane Publishing Co. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=I3HRRrDd1n8C&pg=PA28 |page=28}}
- {{citation |year=2006 |author=ISO 80000-3 |title=Quantities and units |publisher=International Organization for Standardization |volume=Part 3: Space and Time }}
- {{citation |year=2006 |author=Carey |first=W. M. |title=Sound Sources and Levels in the Ocean |journal=IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering |volume=31 }}
- {{citation |year=2007 |author=ISO 80000-8 |title=Quantities and units |publisher=International Organization for Standardization |volume=Part 8: Acoustics }}
- {{citation |year=2013 |author=ANSI/ASA S1.1 |title=Acoustical Terminology |volume=ANSI/ASA S1.1-2013 |publisher=Acoustical Society of America }}
- {{citation |year=2015 |author=Ainslie |first=M. A. |title=A Century of Sonar: Planetary Oceanography, Underwater Noise Monitoring, and the Terminology of Underwater Sound |url=http://acousticstoday.org/a-century-of-sonar-planetary-oceanography-underwater-noise-monitoring-and-the-terminology-of-underwater-sound-michael-a-ainslie/ |journal=Acoustics Today |volume=11 |issue=1 }}
- {{citation |year=2015 |author=D'Amore |first=F. |title=Effect of moisturizer and lubricant on the finger‒surface sliding contact: tribological and dynamical analysis |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/316104462_Effect_of_moisturizer_and_lubricant_on_the_finger-surface_sliding_contact_tribological_and_dynamical_analysis }}
- {{citation |year=2016 |author=IEEE/ASTM SI 10 |title=American National Standard for Metric Practice |publisher=IEEE Standards Association }}
- Fyodor N. Yurchikhin
- Fyodor Okhlopkov
- Fyodorova
- Fyodorovka
- Fyodorovskaya
- Fyodorovskaya Church
- Fyodorovski
- Fyodorovski District
- Fyodorovskii
- Fyodorovskii District
- Fyodorovskii Raion
- Fyodorovski Raion
- Fyodorovskiy
- Fyodorovskiy District
- Fyodorovskiy Raion
- Fyodorovsky
- Fyodorovsky Raion
- Fyodor Pavlovich Reshetnikov
- Fyodor Petrov
- Fyodor Petrovich Tolstoy
- Fyodor Pirotsky
- Fyodor Polishchuk
- Fyodor Raskolnikov
- Fyodor Reshetnikov
- Fyodor Reshetnikov (disambiguation)