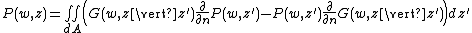- References
The Kirchhoff–Helmholtz integral combines the Helmholtz equation with the Kirchhoff integral theorem[1] to produce a method applicable to acoustics,[2] seismology[3] and other disciplines involving wave propagation.
It states that the sound pressure is completely determined within a volume free of sources, if sound pressure and velocity are determined in all points on its surface.
References
1. ^{{citation |url=http://www.isiweb.ee.ethz.ch/teaching/courses/ak1/acoustics-sound-field-calculations.pdf |title=Acoustics I: sound field calculations |author=Kurt Heutschi |date=2013-01-25}}
2. ^{{citation |url=https://asa.scitation.org/doi/abs/10.1121/1.415524 |publisher=Journal of the Acoustical Society of America |title=The Kirchhoff–Helmholtz integral theorem and related identities for waves in an inhomogeneous moving fluid |author=Oleg A. Godin |date=August 1998}}
3. ^{{citation |url=https://watermark.silverchair.com/72-1-237.pdf?token=AQECAHi208BE49Ooan9kkhW_Ercy7Dm3ZL_9Cf3qfKAc485ysgAAAa8wggGrBgkqhkiG9w0BBwagggGcMIIBmAIBADCCAZEGCSqGSIb3DQEHATAeBglghkgBZQMEAS4wEQQMseCV5XZNFMMGjqTdAgEQgIIBYlxJteZoalNlMMtnpCNLCy5HR1JZfH8M1LdMx1Rgj7Oo3drUqKgXIjbp4oClxzMK0qRZJfqV_11_Vnt6lvX7zbG4G45rKi0fOyP2uR2uGnfyi7zHzJa-v53qmUZ0oKWWeP-HC-ZwkLSdP0WHOzUnbvq3SatF6cDlzO9vk37SwaheW1ulXBRV_nT1yS0wSQtZo13nKhSmJYEN8vSVcSmCPwMNkP99k8a8ell2Io-QCDIe8k9ZVFtiez-Lg9LUeVtjWZWWsxbkxD-9a4S6Y0ARcqgX7dq4KMtd8Y9W-4VVu_ht5wtgcgCPORhVeteaSPU7L3yAaDSjeIxw8-BwZ0CylHVTRleZlk6wclWRpoe7hwIyEfX54nSmX0WiH5oMVMg814v5al2kpA6BbSL75XFDqDIkQ_to3t3wyS1WSy9ShNb8sxuT2NFN_YGl5VV691pIi54_JMCdUvMDAnZnPoVncAUacw |title=Applications of the Kirchhoff-Helmholtz integral to problems in seismology |author1=Patricia Scott |author2=Don Helmberger |date=1983}}
{{DEFAULTSORT:Kirchhoff-Helmholtz integral}}{{physics-stub}}2. ^{{citation |url=https://asa.scitation.org/doi/abs/10.1121/1.415524 |publisher=Journal of the Acoustical Society of America |title=The Kirchhoff–Helmholtz integral theorem and related identities for waves in an inhomogeneous moving fluid |author=Oleg A. Godin |date=August 1998}}
3. ^{{citation |url=https://watermark.silverchair.com/72-1-237.pdf?token=AQECAHi208BE49Ooan9kkhW_Ercy7Dm3ZL_9Cf3qfKAc485ysgAAAa8wggGrBgkqhkiG9w0BBwagggGcMIIBmAIBADCCAZEGCSqGSIb3DQEHATAeBglghkgBZQMEAS4wEQQMseCV5XZNFMMGjqTdAgEQgIIBYlxJteZoalNlMMtnpCNLCy5HR1JZfH8M1LdMx1Rgj7Oo3drUqKgXIjbp4oClxzMK0qRZJfqV_11_Vnt6lvX7zbG4G45rKi0fOyP2uR2uGnfyi7zHzJa-v53qmUZ0oKWWeP-HC-ZwkLSdP0WHOzUnbvq3SatF6cDlzO9vk37SwaheW1ulXBRV_nT1yS0wSQtZo13nKhSmJYEN8vSVcSmCPwMNkP99k8a8ell2Io-QCDIe8k9ZVFtiez-Lg9LUeVtjWZWWsxbkxD-9a4S6Y0ARcqgX7dq4KMtd8Y9W-4VVu_ht5wtgcgCPORhVeteaSPU7L3yAaDSjeIxw8-BwZ0CylHVTRleZlk6wclWRpoe7hwIyEfX54nSmX0WiH5oMVMg814v5al2kpA6BbSL75XFDqDIkQ_to3t3wyS1WSy9ShNb8sxuT2NFN_YGl5VV691pIi54_JMCdUvMDAnZnPoVncAUacw |title=Applications of the Kirchhoff-Helmholtz integral to problems in seismology |author1=Patricia Scott |author2=Don Helmberger |date=1983}}
1 : Acoustic equations
- Arcane Jill Watson
- Arcane literature (Cthulhu mythos)
- Arcane Rain Fell
- Arcane School
- Arcane Trickster
- Arcangel
- Arcangela Tarabotti
- Arcangel & De la Ghetto
- Arcangelo Califano
- Arcangelo Felice Assunta Wertmuller von Elgg
- Arcangelo Ghisleri
- Arcangelo Resani
- Arc Angels
- Arcangel y de la ghetto
- Arcangues
- Arcangues (horse)
- Arcanobacterium haemolyticum
- Arcanoceras
- Arcanoid
- Arcanum (album)
- Arcanum (Book)
- Arcanum (comic)
- Arcanum (disambiguation)
- Arcanum duplicatum
- Arcanum High School