- Applicable to/under conditions
- Coverage
- Mathematical formulation The model Calculation of reference path loss Calculation of adjustment factors The base station antenna height correction factor The base station antenna gain correction factor The mobile station antenna height correction factor The mobile antenna gain correction factor The frequency correction factor Effective terrain slope calculation
- See also
- References
The Lee model for point-to-point mode is a radio propagation model that operates around 900 MHz. Built as two different modes, this model includes an adjustment factor that can be adjusted to make the model more flexible to different regions of propagation.[1]
Applicable to/under conditions
This model is suitable for using in data collected in a specific area for point-to-point links.
Coverage
Frequency: 900 MHz band
Mathematical formulation
The model
The Lee model for point to point mode is formally expressed as:
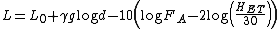
where,
L = The median path loss. Unit: decibel (dB)
L0 = The reference path loss along 1 km. Unit: decibel (dB)
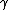 = The slope of the path loss curve. Unit: decibels per decade
= The slope of the path loss curve. Unit: decibels per decade
d = The distance on which the path loss is to be calculated. Unit: kilometer (km)
FA = Adjustment factor.
HET = Effective height of terrain. Unit: meter(m)
Calculation of reference path loss
The reference path loss is usually computed along a 1 km or 1 mi link. Any other suitable length of path can be chosen based on the applications.
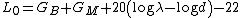
where,
GB = Base station antenna gain. Unit: Decibel with respect to isotropic antenna (dBi)
 = Wavelength. Unit: meter (m).
= Wavelength. Unit: meter (m).
GM = Mobile station antenna gain. Unit: decibel with respect to isotropic antenna (dBi).
Calculation of adjustment factors
The adjustment factor is calculated as:
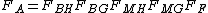
where,
FBH = Base station antenna height correction factor.
FBG = Base station antenna gain correction factor.
FMH = Mobile station antenna height correction factor.
FMG = Mobile station antenna gain correction factor.
FF = Frequency correction factor
The base station antenna height correction factor
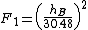
where,
hB = Base station antenna height. Unit: meter.
The base station antenna gain correction factor
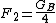
where,
GB = Base station antenna gain. Unit: decibel with respect to half-wave dipole (dBd)
The mobile station antenna height correction factor
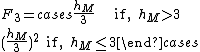
where,
hM = Mobile station antenna height. Unit: meter.
The mobile antenna gain correction factor
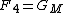
where,
GM = Mobile station antenna gain. Unit:Decibel with respect to half wave dipole antenna (dBd).
The frequency correction factor
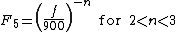
where,
f = Frequency. Unit: megahertz (MHz)
Effective terrain slope calculation
This is computed in the following way:
- Extrapolate terrain slope at the mobile station to the base station.
- Compute the vertical antenna height over the extrapolation line.
See also
- Hata model for urban areas
- Hata model for suburban areas
- Hata model for open areas
- Okumura model for urban areas
- COST 231 model
- Young model
- Area-to-area Lee model
References
- Buyant Ukha Airport
- Buyantu Khan
- Buy.com Tour
- Buyeo
- Buyeo County
- Buyeo (disambiguation)
- Buyeo languages
- Buyeo Pung
- Buyeo Yung
- Buyer
- Buyer Beware
- Buyer beware
- Buyer decision process
- Buyer leverage
- Buyer's agent
- Buyers agent
- Buyers laboratory
- Buyer's Laboratory
- Buyers Laboratory Inc
- Buyi
- Buyid
- Buyid dynasty
- Buyids
- Buyin
- Buying