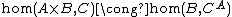- Examples Functional programming APL family Stack-based UNIX pipeline
- See also
- References
- External links
UNIX scripting uses the paradigm with pipes.
For example, a sequence of operations in an applicative language such as the following Python code:
def example(x):
y = foo(x) z = bar(y) w = baz(z) return w
... is written in point-free style as the composition of a sequence of functions, without parameters:[3]
def flow(fns):
def reducer(v, fn): return fn(v)
example = flow([baz, bar, foo])
The key idea in tacit programming is to assist in operating at the appropriate level of abstraction. That is, to translate the natural transformation given by currying
into computer functions, where the left represents the uncurried form of a function and the right the curried. CA denotes the functionals from A to C (see also exponential object), while A × B denotes the Cartesian product of A and B.
Examples
Functional programming
A simple example (in Haskell) is a program which takes a sum of a list. A programmer might define a sum recursively using a pointed (cf. value-level programming) method as:
sum (x:xs) = x + sum xs
sum [] = 0
However, by noting this as a fold the programmer could replace this with:
sum xs = foldr (+) 0 xs
And then the argument is not needed, so this can be replaced with
sum = foldr (+) 0
which is point-free.
Another example uses the dot operator:
p x y z = f (g x y) z
The following Haskell-like pseudo-code exposes how to reduce a function definition to its point-free equivalent:
p = \\x -> \\y -> \\z -> f (g x y) z
= \\x -> \\y -> f (g x y) = \\x -> \\y -> (f . (g x)) y = \\x -> f . (g x) = \\x -> ((.) f) (g x) = \\x -> (((.) f) . g) x = ((.) f) . g
so
p = ((.) f) . g
Finally, to see a complex example imagine a map filter program which takes a list, applies a function to it, and then filters the elements based on a criterion
mf criteria operator list = filter criteria (map operator list)
It can be expressed point-free[4] as
mf = (. map) . (.) . filter
APL family
In J, the same sort of point-free code occurs in a function made to compute the average of a list (array) of numbers:
+/ sums the items of the array by mapping (/) summation (+) to the array. % divides the sum by the number of elements (#) in the array.
Euler's formula expressed tacitly:
cos =: 2 o. ]
sin =: 1 o. ]
Euler =: ^@j. = cos j. sin
(j. is a primitive function whose monadic definition is 0j1 times x and whose dyadic definition is x+0j1×y.) The same tacit computations expressed in Dyalog APL:
avg ← +⌿ ÷ ≢
cos ← 2 ○ ⊢
sin ← 1 ○ ⊢
j ← {⍺←0 ⋄ ⍺+0j1×⍵} ⍝ this part is not tacit
Euler ← *∘j = cos j sin
Stack-based
In stack-oriented programming languages (and concatenative ones, most of which are stack based), point-free methods are commonly used. For example, a procedure to compute the Fibonacci numbers might look like the following in PostScript:
/fib { dup dup 1 eq exch 0 eq or not { dup 1 sub fib exch 2 sub fib add } if } defUNIX pipeline
{{main|Pipeline (Unix)}}In UNIX scripting the functions are computer programs which receive data from standard input and send the results to standard output. For example,
sort | uniq -c | sort -rn
is a tacit or point-free composition which returns the counts of its arguments and the arguments, in the order of decreasing counts. The 'sort' and 'uniq' are the functions, the '-c' and '-rn' control the functions, but the arguments are not mentioned. The '|' is the composition operator.
See also
- Combinatory logic
- Concatenative programming language
- Function-level programming
- Joy (programming language), modern highly tacit language
- Pointless topology
References
2. ^W. Neville Holmes, ed. (2006) Computers and People
3. ^{{cite web | url=http://concatenative.org/wiki/view/Concatenative%20language/Name%20code%20not%20values | title=Name code not values | publisher=Concatenative.org | accessdate=13 September 2013}}
4. ^pipermail
5. ^{{Cite web|url=https://wiki.haskell.org/Pointfree#But_pointfree_has_more_points.21|title=Pointfree - HaskellWiki|website=wiki.haskell.org|access-date=2016-06-05}}
External links
- Pure Functions in APL and J How to use tacit programming in any APL-like language
- Riddell Nunataks
- Riddel Viper
- Ridder
- Ridder Arena
- Ridderbuurt
- Ridder, Kazakhstan
- Ridderschap
- Ridderschap of Holland
- Ridderschap van Holland
- Ridder (title)
- Ridderzaal
- Riddes
- Riddes, Switzerland
- Riddes (Valais)
- Riddes VS
- Riddhi
- Riddick Bowe Boxing
- Riddick Parker
- Riddick's Senate Procedure
- Riddick Stadium
- Riddick stadium
- Riddim Wise
- Riddim Wise LP
- Riddlecombe
- Riddle contest