乳油制备manufacture of emulsifiable con-centrates
用农药原药、乳化剂、有机溶剂经混溶工艺,制成乳油,贮存备用的过程。乳油制备所需的设备简单,投资不多,配制技术易掌握,基本上没有“三废”。
原料选用 主要是原药、有机溶剂、乳油的选用。❶农药原药。应选用在有机溶剂中溶解度较大的农药品种。一般来说,凡是油溶性或有机性比较强的原油,在油中溶解度大。凡是水溶性或无机性比较强的固体原粉,如含有各种杂环结构的农药品种,在油中的溶解度小,加工制成乳油就比较困难。
❷有机溶剂常选用二甲苯、甲苯等芳香烃类化合物。因其资源丰富、价格便宜、溶解能力好,不易引起有效成分的分解。
❸乳化剂。要使乳油具有在水中自行分散的能力,就必须加用阴离子表面活性剂十二烷基苯磺酸钙(以下简称钙盐)。常用的农药乳化剂都是非离子表面活性剂与钙盐的复配制剂。一般混合型乳化剂的配方中,非离子表面活性剂占80~60%,钙盐占20~40%。在这个配比范围内进行乳化试验找出适当的配比以确定钙盐的最适用量。非离子表面活性剂的选用,对大多数有机磷农药品种,应选用以多苯核为母体的醚型表面活性剂为主体,如BP型乳化剂( 二苄基苯酚聚氧乙烯醚),农乳600号乳化剂[三(苯乙基)苯酚聚氧乙烯醚],BC型乳化剂(二苄基复酚聚氧乙烯醚),BS型乳化剂[二(苯乙基)复酚聚氧乙烯醚]等。对大多数有机氯农药品种,应选用BY型乳剂(蓖麻油聚氧乙烯醚),OP型乳化剂(烷基酚聚氧乙烯醚)等乳化剂单体与钙盐的混合型复配乳化剂。一般用量为6~10%。
❹其他成分。如助溶剂、稳定剂等。
制备方法 一般包括4个步骤:❶有效成分含量的选定。主要取决于原药在有机溶剂中的溶解度。一般制成50~80%乳油。某些特殊用途或高效农药产品,有效成分含量可以降低。如2.5%溴氰菊酯乳油。
❷调制工艺。调制乳油的主要设备是调制釜。它是由带夹套的搪瓷玻璃反应釜、搅拌器和冷凝器等组成(见图)。如果原药在常温下是流动性能好的液体,可按照选定的配方,将原药、乳化剂和溶剂依次投入调制釜中,开动搅拌机进行混溶,一般情况下不需要加热或冷却。但在冬季较冷的地区,或夏季较热的地区,要根据气温变化情况适当加热或冷却。如果原药是固体或常温下流动性较差的液体,可先将原药和大部分溶剂投入调制釜,在搅拌下使原药溶解在溶剂中。有时为了加快原药的溶解速度,可以适当加热,但加热温度不应高于溶剂的沸点。待原药全部溶解后(如当时温度较高,须适当冷却),再投入乳化剂和剩余的溶剂。继续搅拌直至混合均匀。
❸调整。混合均匀后的物料,将温度调节到室温,取样分析有效成分含量、水分、pH值以及乳化性能等项指标。如不合格,应进行调整。
❹包装。用灌装机进行全自
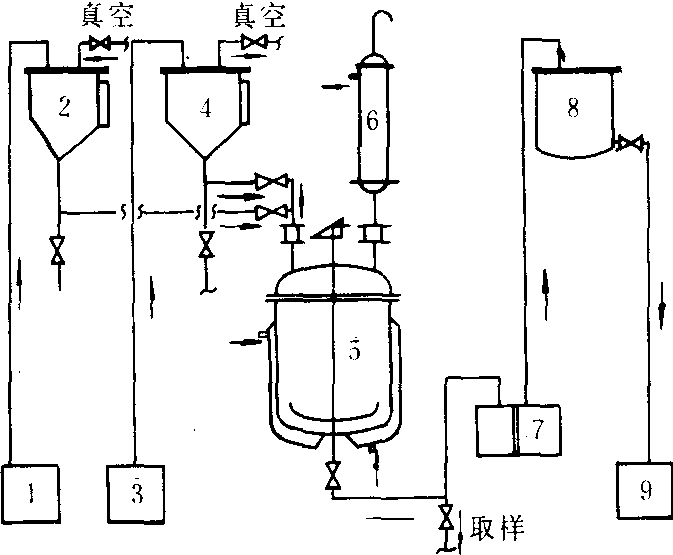
乳油调制工艺图
(据华世豪等)
1.农药原油;2.原油计量槽;3.溶剂;4.溶剂计量槽;5.调制釜;6.冷凝器;7.过滤器;8.乳油贮槽;9.成品包装