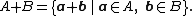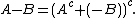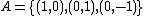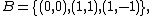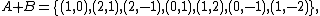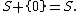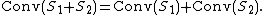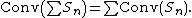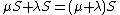- Example
- Convex hulls of Minkowski sums
- Lp Minkowski sum
- See also
- Notes
- References
- External links
In geometry, the Minkowski sum (also known as dilation) of two sets of position vectors A and B in Euclidean space is formed by adding each vector in A to each vector in B, i.e., the set
Analogously, the Minkowski difference (or geometric difference)[1] is defined as
It is important to note that in general 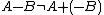 . For instance, in a one-dimensional case
. For instance, in a one-dimensional case 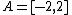 and
and 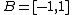 the Minkowski difference
the Minkowski difference 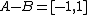 , whereas
, whereas 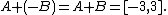 The correct formula connecting Minkowski sum and difference is as follows (here
The correct formula connecting Minkowski sum and difference is as follows (here 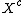 stands for the complement of
stands for the complement of 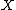 ):
):
In a two-dimensional case, Minkowski difference is closely related to erosion (morphology) in image processing.
The concept is named for Hermann Minkowski.
Example
For example, if we have two sets A and B, each consisting of three position vectors (informally, three points), representing the vertices of two triangles in 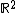 , with coordinates
, with coordinates
and
then their Minkowski sum is
which comprises the vertices of a hexagon.
For Minkowski addition, the zero set, {0}, containing only the zero vector, 0, is an identity element: for every subset S of a vector space,
The empty set is important in Minkowski addition, because the empty set annihilates every other subset: for every subset S of a vector space, its sum with the empty set is empty:
Convex hulls of Minkowski sums
Minkowski addition behaves well with respect to the operation of taking convex hulls, as shown by the following proposition:
- For all non-empty subsets S1 and S2 of a real vector space, the convex hull of their Minkowski sum is the Minkowski sum of their convex hulls:
This result holds more generally for any finite collection of non-empty sets:
In mathematical terminology, the operations of Minkowski summation and of forming convex hulls are commuting operations.[2][3]
If {{mvar|S}} is a convex set then 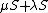 is also a convex set; furthermore
is also a convex set; furthermore
for every 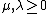 . Conversely, if this "distributive property" holds for all non-negative real numbers,
. Conversely, if this "distributive property" holds for all non-negative real numbers, 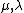 , then the set is convex.[4]
, then the set is convex.[4]
The figure shows an example of a non-convex set for which {{math|A + A ⊋ 2A}}|title=General competitive analysis|publisher=North-Holland||series=Advanced textbooks in economics|volume=12|edition=reprint of (1971) San Francisco, CA: Holden-Day, Inc. Mathematical economics texts. 6|location=Amsterdam|isbn=978-0-444-85497-1|mr=439057|ref=harv}}
|author=Henry Mann |authorlink=Henry Mann
|title=Addition Theorems: The Addition Theorems of Group Theory and Number Theory
|publisher=Robert E. Krieger Publishing Company
|via=http://www.krieger-publishing.com/subcats/MathematicsandStatistics/mathematicsandstatistics.html
|location=Huntington, New York
|year=1976
|edition=Corrected reprint of 1965 Wiley
|isbn=978-0-88275-418-5
}}
- {{cite book|last=Rockafellar|first=R. Tyrrell|authorlink=R. Tyrrell Rockafellar|title=Convex analysis|edition=Reprint of the 1979 Princeton mathematical series 28|series=Princeton landmarks in mathematics|publisher=Princeton University Press|location=Princeton, NJ|year=1997|pages=xviii+451|isbn=978-0-691-01586-6|mr=1451876|ref=harv}}
- {{Citation |first=Melvyn B. |last=Nathanson |title=Additive Number Theory: Inverse Problems and Geometry of Sumsets |series=GTM |volume=165 |publisher=Springer |year=1996 |zbl=0859.11003 }}.
- {{Citation |last=Oks |first=Eduard |last2=Sharir |first2=Micha |year=2006 |title=Minkowski Sums of Monotone and General Simple Polygons |journal=Discrete and Computational Geometry |volume=35 |issue=2 |pages=223–240 |doi=10.1007/s00454-005-1206-y }}.
- {{Citation |first=Rolf |last=Schneider |title=Convex bodies: the Brunn-Minkowski theory |publisher=Cambridge University Press |location=Cambridge |year=1993 |isbn= }}.
- {{Citation |first=Terence |last=Tao |lastauthoramp=yes |first2=Van |last2=Vu |title=Additive Combinatorics |publisher=Cambridge University Press |year=2006 |isbn= }}.
- {{cite journal | last1 = Mayer | first1 = A. | last2 = Zelenyuk | first2 = V. | year = 2014 | title = Aggregation of Malmquist productivity indexes allowing for reallocation of resources | url = https://ideas.repec.org/a/eee/ejores/v238y2014i3p774-785.html | journal = European Journal of Operational Research | volume = 238 | issue = 3| pages = 774–785 | doi=10.1016/j.ejor.2014.04.003}}
- {{cite journal | last1 = Zelenyuk | first1 = V | year = 2015 | title = Aggregation of scale efficiency | url = https://ideas.repec.org/a/eee/ejores/v240y2015i1p269-277.html | journal = European Journal of Operational Research | volume = 240 | issue = 1| pages = 269–277 | doi=10.1016/j.ejor.2014.06.038}}
External links
- {{springer|title=Minkowski addition|id=p/m120210}}
- {{citation|title=On the tendency toward convexity of the vector sum of sets|authorlink=Roger Evans Howe|last=Howe|first=Roger|year=1979|publisher=Cowles Foundation for Research in Economics, Yale University|series=Cowles Foundation discussion papers|volume=538|url=http://econpapers.repec.org/RePEc:cwl:cwldpp:538}}
- Minkowski Sums, in Computational Geometry Algorithms Library
- The Minkowski Sum of Two Triangles and The Minkowski Sum of a Disk and a Polygon by George Beck, The Wolfram Demonstrations Project.
- Minkowski's addition of convex shapes by Alexander Bogomolny: an applet
- OpenSCAD User Manual/Transformations#minkowski by Marius Kintel: Application
- T s diagram
- T-s diagram
- Ts diagram
- TS diagram
- TS (disambiguation)
- TSDOLE
- TsDPEN
- T.s.durairaj
- T. S. Durairaj
- TSE1
- Tse1
- TS-E24mm f/3.5L
- Tseajaia
- Tseajaiidae
- Tsearch
- TSearch
- Tse Bii' Ndzisgaii
- Tseboum Soumdo
- Tsebrykove
- TSE buffer
- TSEC (disambiguation)
- Tsechen Dzong
- Tsechen Monastery
- Tsechen Monastery and Dzong
- Tsedaka