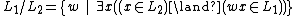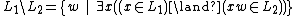- Example
- Properties
- See also
- References
In mathematics and computer science, the right quotient (or simply quotient) of a formal language  with a formal language
with a formal language  is the language consisting of strings w such that wx is in
is the language consisting of strings w such that wx is in  for some string x in
for some string x in  .[1] In symbols, we write:
.[1] In symbols, we write:
In other words, each string in 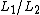 is the prefix of a string
is the prefix of a string 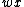 in
in  , with the remainder of the word being a string in
, with the remainder of the word being a string in  .
.
Similarly, the left quotient of  with
with  is the language consisting of strings w such that xw is in
is the language consisting of strings w such that xw is in  for some string x in
for some string x in  . In symbols, we write:
. In symbols, we write:
The left quotient can be regarded as the set of postfixes that complete words from  , such that the resulting word is in
, such that the resulting word is in  .
.
Example
Consider
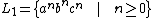
and
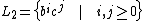 .
.
Now, if we insert a divider into the middle of an element of  , the part on the right is in
, the part on the right is in  only if the divider is placed adjacent to a b (in which case i ≤ n and j = n) or adjacent to a c (in which case i = 0 and j ≤ n). The part on the left, therefore, will be either
only if the divider is placed adjacent to a b (in which case i ≤ n and j = n) or adjacent to a c (in which case i = 0 and j ≤ n). The part on the left, therefore, will be either 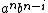 or
or 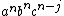 ; and
; and 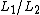 can be written as
can be written as
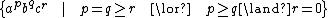 .
.Properties
Some common closure properties of the right quotient include:
- The quotient of a regular language with any other language is regular.
- The quotient of a context free language with a regular language is context free.
- The quotient of two context free languages can be any recursively enumerable language.
- The quotient of two recursively enumerable languages is recursively enumerable.
These closure properties hold for both left and right quotients.
See also
- Brzozowski derivative
References
- List of Presidents of Guinea
- List of Presidents of Guinea-Bissau
- List of presidents of Haiti
- List of Presidents of Honduras
- List of Presidents of Hungary
- List of Presidents of Iceland
- List of Presidents of India
- List of Presidents of Indonesia
- List of Presidents of Iran
- List of presidents of iran
- List of Presidents of Iraq
- List of Presidents of Ireland
- List of Presidents of Italy
- List of Presidents of Kenya
- List of Presidents of Lebanon
- List of Presidents of Lithuania
- List of Presidents of Malawi
- List of presidents of Mexico
- List of Presidents of Mozambique
- List of Presidents of Namibia
- List of Presidents of Nicaragua
- List of Presidents of Niger
- List of Presidents of Nigeria
- List of Presidents of North Yemen
- List of Presidents of Pakistan