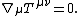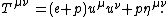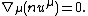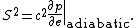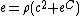- See also
In fluid mechanics and astrophysics, the relativistic Euler equations are a generalization of the Euler equations that account for the effects of special relativity.
The equations of motion are contained in the continuity equation of the stress–energy tensor 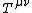 :
:
For a perfect fluid,
Here  is the relativistic rest energy density of the fluid,
is the relativistic rest energy density of the fluid,  is the fluid pressure,
is the fluid pressure, 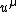 is the four-velocity of the fluid, and
is the four-velocity of the fluid, and 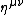 is the Minkowski metric tensor with signature {{math|(−,+,+,+)}}.
is the Minkowski metric tensor with signature {{math|(−,+,+,+)}}.
To the above equations, a statement of conservation is usually added, usually conservation of baryon number. If  is the number density of baryons this may be stated
is the number density of baryons this may be stated
These equations reduce to the classical Euler equations if the fluid three-velocity is much less than the speed of light, the pressure is much less than the energy density, and the latter is dominated by the rest mass density.
The relativistic Euler equations may be applied to calculate the speed of sound in a fluid with a relativistic equation of state (that is, one in which the pressure is comparable with the internal energy density  , including the rest energy;
, including the rest energy; 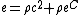 where
where 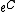 is the classical internal energy per unit mass).
is the classical internal energy per unit mass).
Under these circumstances, the speed of sound  is given by
is given by
(note that
is the relativistic internal energy density). This formula differs from the classical case in that  has been replaced by
has been replaced by 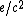 .
.
See also
- Relativistic heat conduction
- Equation of state (cosmology)
- Peter Johnstone (footballer)
- Peter Johnston, Jr.
- Peter Johnston (politician)
- Peter Johnston (rugby league)
- Peter Johnston (rugby league, born 1968)
- Peter Johnston (Wisconsin politician)
- Peter John Uglietto
- Peter John Webster
- Peter Jok
- Peter J. Olver
- Peter J Olver
- Peter Jonathan Hitchens
- Peter Jonathan Wilcox
- Peter Jones (Australian politician)
- Peter Jones (businessman)
- Peter Jones (cricketer, born 1948)
- Peter Jones (journalist)
- Peter Jones (paediatrician)
- Peter Jones (sugeon)
- Peter Jones (surgeon)
- Peter Joplin Commercial Block
- Peter Jordan
- Peter Jordan (actor)
- Peter Jordan (disambiguation)
- Peter Jory