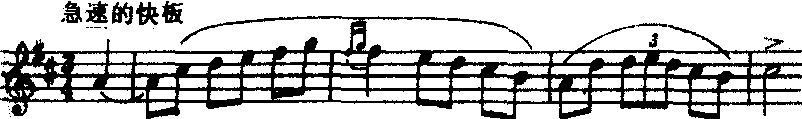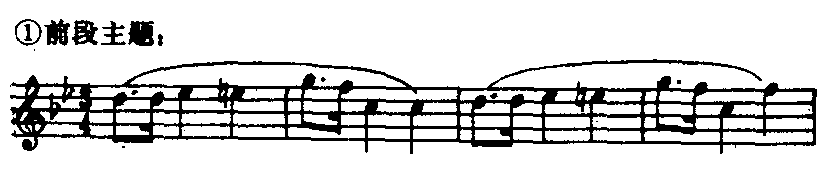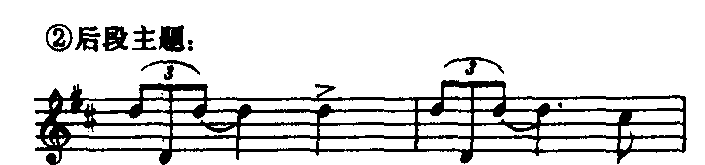D大调玛祖卡
钢琴曲。波兰作曲家肖邦1837~1838年间所写的60余首“玛祖卡”舞曲钢琴曲的第23首。在肖邦大量的钢琴作品中,玛祖卡舞曲最具民族特色。他的“玛祖卡舞曲”是在“玛祖尔”、“奥别列克”及“库亚维亚克”三种波兰民间舞曲的基础上形成的。这三种舞曲皆为3拍子,但节奏和重音位置不同,各具不同的特点:“玛祖尔”热情欢快,重音强烈而多变,可自由落在任何一拍上,但常见的是落在第二拍;“奥别列克”活泼、急速,带有突然转弯,具有戏剧和幽默性,重音在双数小节的第三拍上;“库亚维亚克”从容不迫,节奏平稳,重音分布比“奥别列克”自由,但严格遵守反复的原则。肖邦的“玛祖卡舞曲”常用这三种舞曲的不同特点形成鲜明的对比而丰富多采。《D大调玛祖卡》是一首优美典雅的舞曲。由复三段体写成。第一部分的主题是根据“库亚维亚克”舞曲的特点写成。上下起伏所形成的波浪式的旋律线,委婉流畅,充满生气。