三角洲sanjiaozhou
河流入海或入湖的河口地区,坡度变缓,流速减小,同时受到河口的各种地质作用,沉积物大量堆积,形成一片平坦的低地,其平面形态往往象希腊字母“Δ”,故称三角洲。形成三角洲的条件:❶河流携带丰富的泥沙;
❷河口沿岸无强大的波浪和海流作用;此外,地壳运动、基面变化、气候变迁、人类活动等对三角洲发育都有影响。三角洲的形态有以下几种:❶尖头形三角洲:河流入海或入湖时,只有一条主流,或有支流但规模不大,泥沙在河口处堆积成沙嘴,形成明显向海突出的尖头形三角洲,例如意大利的台伯河等(图1)。
❷扇形三角洲:河流泥沙丰富,河口以外海滨水浅的情况下形成的。三角洲上汊河众多,分汊顶点向海呈放射状水系,新老水道交织如网。由于河口泥沙的堆积,使河床纵比降减小,径流宣泄不畅,洪水时汊河极易改道,使三角洲岸线向海推进,形成扇形三角洲,如黄河三角洲和尼罗河三角洲(图2、3)。
❸鸟爪形三角洲:在弱潮河口,没有强大的沿岸流,河流作用占绝对优势,挟带丰富沙泥的河流分成几股从不同方向入海,因波浪和潮汐作用微弱,三角洲上的分流水道向海伸出较长的沙嘴,从整体看形如鸟爪,称鸟爪形三角洲,如密西西比河三角洲(图4)。三角洲地势低平,河网密集,土壤肥沃,大多是良好的农耕地区
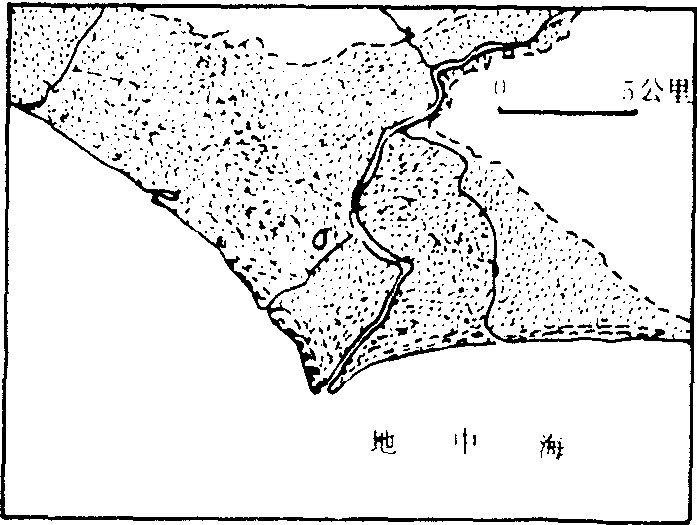
图1 台伯河三角洲
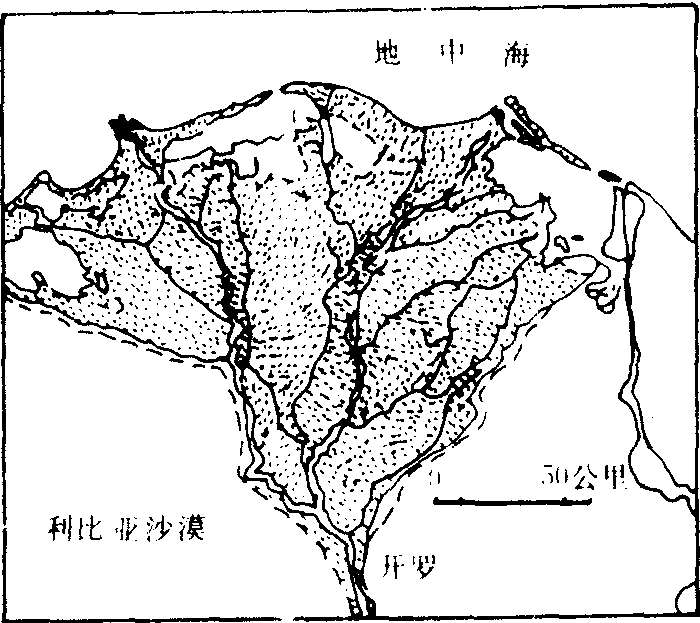
图2 尼罗河三角洲
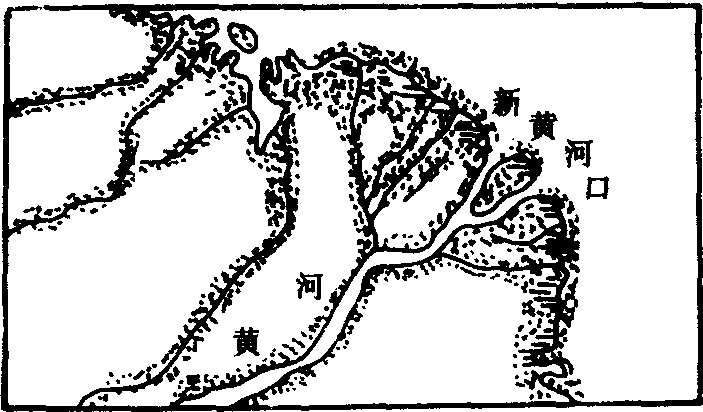
图3 黄河三角洲
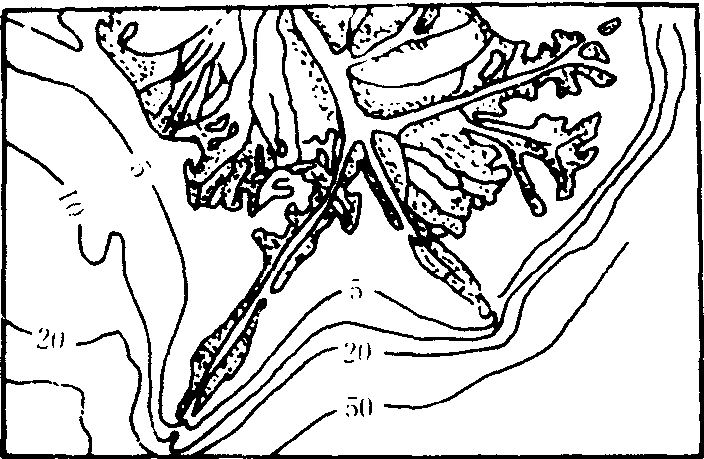
图4 密西西比河三角洲
三角洲Sanjiaozhou
在河流入海或入湖的河口地段,由于河流和海洋或湖泊的相互作用,使大量碎屑物质发生沉积,形成大片低地,其平面形态好似一个尖端向着陆地的三角形,称为三角洲。三角洲的发育,主要取决于河口地区水流变化的基本规律。河流、海洋、构造、气候和流域自然地理因素等,都在不同程度上影响着三角洲的沉积特征和形态类型。形成三角洲的必须条件是:❶河流带来大量泥沙。据统计,河流年输沙量与年径流量的比值大于0.24可能形成三角洲,小于0.24则往往发育成三角港。
❷河口附近海洋(或湖)的搬运侵蚀能力较小,河流搬运来的泥沙等物质不至于被波浪、潮流带走,能在河口附近沉积。
❸河口外海(湖)滨区地势平坦,海水较浅,有利于泥沙堆积。三角洲的形成过程比较复杂。在河口地区水流比降小,水面展宽,河口和海(湖)水混合,流速急剧降低,使大量泥沙迅速堆积,首先形成河口沙坝、心滩、沙洲,在河口两侧形成河口沙嘴或水下天然堤。沉积物在沉降过程中发生分异,向海越远颗粒越细。由于河口沙坝的出现与发展,大大缩小了河流入海的过水断面,迫使河流分汊,形成汊道,新的汊河口又会再产生河口沙坝,又出现新的汊道,这样在河口处汊河、沙坝不断出现,并使许多心滩沙洲合并、增高、向海扩展,并出露水面成为河口沙岛,如长江口的崇明岛。河口沙岛、废弃的汊河道、天然堤、沼泽、洼地等连结成片就是河口三角洲平原,它与向海延伸的水下三角洲紧密相连,构成一个完整的三角洲沉积体系。如北美密西西比河三角洲的扩展,主要是依靠汊河道决口形成决口扇,河流在洪水期决口改道,由新的汊道入海,形成新的三角洲,全新世的密西西比河三角洲由16个这样的亚三角洲组合而成(如图1)。原苏联的伏尔加河三角洲大小汊道500余条。
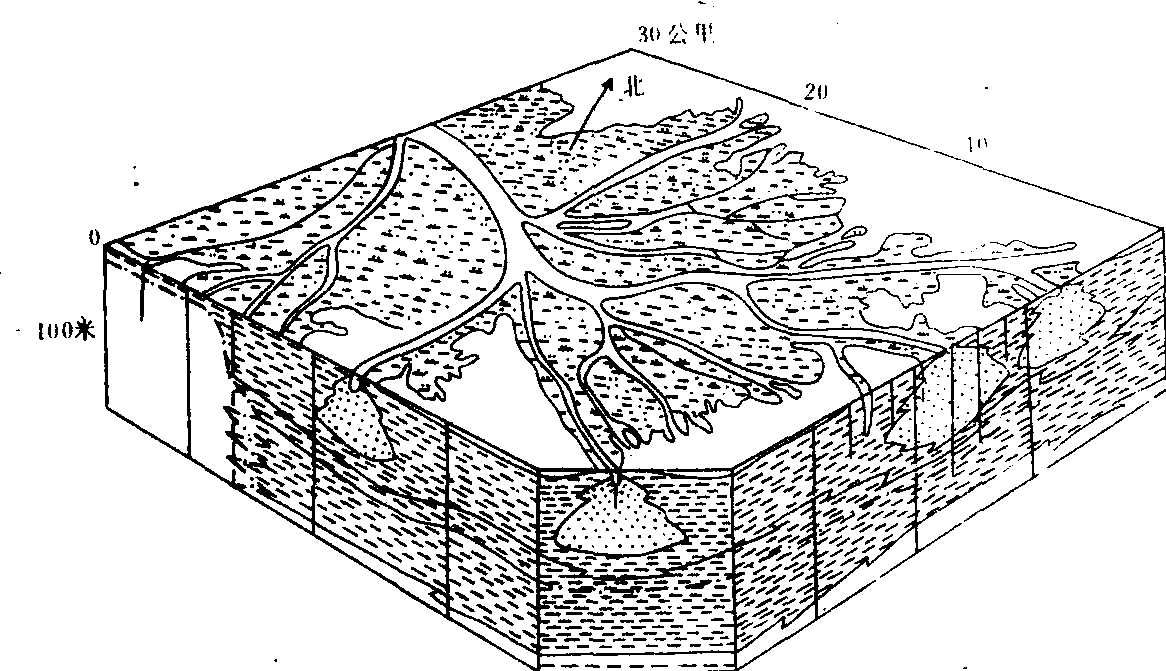
图1 密西西比河三角洲断块剖面图
三角洲的类型复杂多样,可从不同角度进行分类。根据形态特征和形成过程可分为以下几种类型:❶扇形三角洲:入海河流含沙量高,河道分汊多且经常改道,河口外海水较浅,使三角洲形成过程中能比较均匀地向海推进。如我国的黄河三角洲。黄河水的含沙量很大,中、下游的平均含沙量为25.3公斤/米3,中上游每年输沙量为16亿吨,经河口入海的泥沙约12亿吨,其含沙量是长江的47倍,是密西西比河的42倍,是亚马逊河的360倍。自1855年以来形成了面积5 932.6平方公里的现代黄河三角洲,每年以200—2 000米的速度向海推进。从1855年黄河改道由利津入海以来,三角洲已向海推进了约50公里(图2.C)。
❷鸟爪形三角洲:在潮流、海流和波浪作用都很微弱的河口区,河流含沙量较高并分几股汊河入海,各汊河口泥沙迅速堆积,形成向海伸展较长的沙嘴,平面形态很像鸟爪,故称鸟爪形三角洲,以美国密西西比河三角洲最为典型(图1)。
❸尖头形三角洲:河流入海(湖)时,只有一条干流,支流很少或很小,在干流河口处形成向海中突出的尖头形三角洲。如意大利的台伯河三角洲(图2.B1)和西班牙的埃布罗河三角洲。如果河流泥沙较少,岸边海水较深,波浪方向与海岸斜交,则形成河口内堆积的掩闭形三角洲,如非洲南端的奥伦治河三角洲(图2.B2)。
❹岛屿形三角洲:在潮汐作用较强、河流含沙量不高的河口区,在潮水作用下,形成许多向海伸延的垄状沙滩和沙坝,沙坝之间被潮汐冲成水道,使沙洲、沙岛及汊河交错分布、河口外岛屿星罗棋布,故称岛屿形三角洲,如恒河三角洲。我国的长江三角洲从大轮廓上看应是尖头形三角洲(图2.A),但在河口区有许多沙岛、浅滩及汊河道,有人又把它归到岛屿形三角洲之内。三角洲地区地势平坦,土地肥沃,灌溉方便,是发展农业的好地方。在三角洲的沉积过程中,大量的有机质碎屑和淤泥,经过长期地质作用能形成丰富的石油和天然气。如美国的密西西比河三角洲、意大利的波河三角洲、原苏联的伏尔加河三角洲都含有丰富的油气资源。我国在黄河等几条大河河口的三角洲上也发现相当规模的油气田。
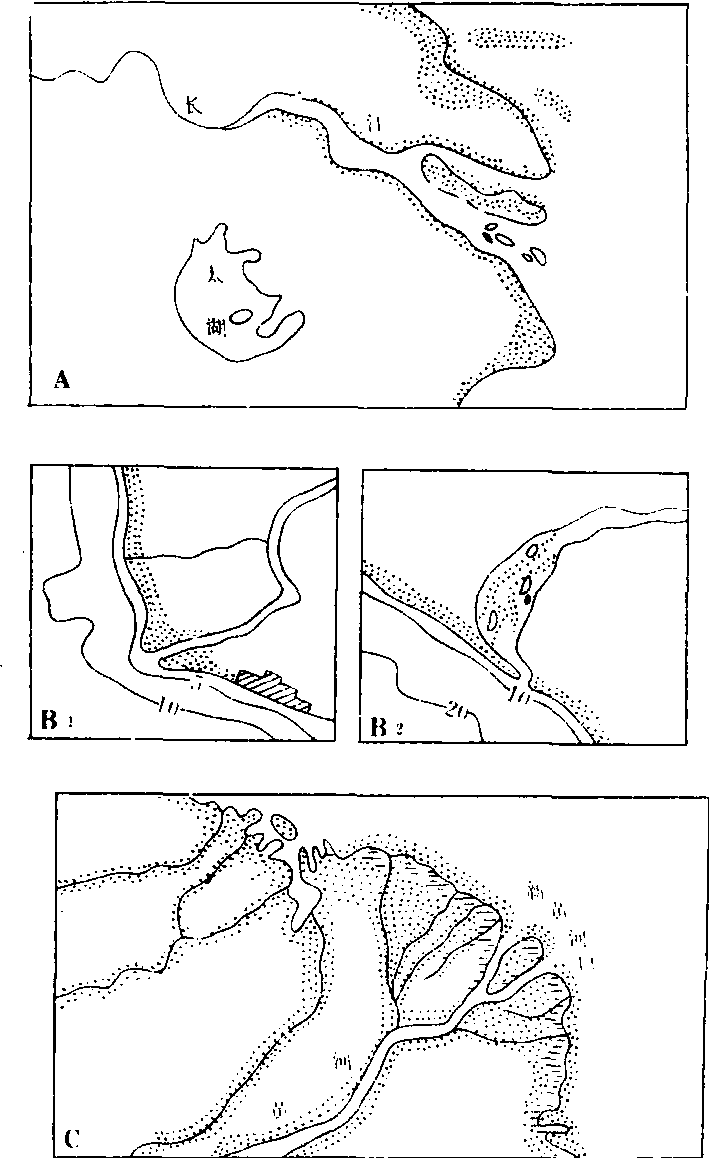
图2 三角洲的类型
A:尖头形三角洲(长江三角洲) B1:尖头形三角洲(意大利台伯河三角洲) B2:掩闭形三角洲(南非奥伦治河三角洲) C:扇形三角洲(黄河三角洲)
三角洲
见“海洋学”中的“三角洲”。
三角洲
入海河口地区的冲积平原。河流在流入海洋或湖泊时,因流速降低,由所携泥沙堆积而成。一般呈三角形或弓形,顶端指向上游,底部为其外缘。地势低平,河流多汊道,河网密集,大部分为良好的农耕地区。如中国的珠江、长江和非洲的尼罗河等河口的三角洲。