水的离子积shui de liziji
水是一种极弱的电解质,产生微弱的电离:
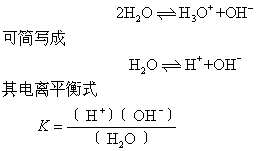
式中K——水的电离平衡常数。因电离极少,水的浓度〔H2O〕可视为常数。上式中〔H+〕〔OH-〕亦可视为常数,令它为Kw,则:
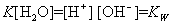
Kw称为水的离子积。
因一般蒸馏水中溶有空气中的CO2等物质,其电导率值约为10-2~10-3S·m-1。F.W.G.柯尔劳施在25℃时测定极纯的水的电导率,得
k=0.055×10-4 S·m-1
又1mol纯水的体积为1.802×10-5m3,则水的摩尔电导率为

由表查得水完全电离时的摩尔电导率为

又1 L水的质量可近似为1000g,水的摩尔质量为18.02g,1L水中水的物质的量浓度为1000/18.02=55.5mol·L-1
则〔H+〕=〔OH-〕 =cα=55.5×1.8×10-9
=1.0×10-7 mol·L-1
故 Kw= 〔H+〕 〔OH-〕 =1.0×10-14 mol2·L2
水的离子积只受温度的影响,温度升高,Kw值增大 (见下表)。
水的离子积 mol2·L-2
| t/℃ | Kw | t/℃ | Kw |
| 0 10 25 | 0.113×10-14 0.292×10-14 1.008×10-14 | 30 40 50 | 1.468×10-14 2.917×10-14 5.74×10-14 |
水的离子积通常采用KW=1.0×10-14mol2·L-2,因而在纯水中 [H+] = [OH-] =1.0×10-7mol·L-1。
对稀的碱或酸溶液,水的离子积仍然适用,即在碱溶液或酸溶液中 [H+] 和 [OH-] 之间的关系也是 [H+] [OH-] =1.0×10-14。因碱或酸在水中离解时,同时产生与其相应的共轭酸或共轭碱,即碱与共轭酸或酸与共轭碱同时存在。如NH+4是酸,则它的共轭碱是NH3,则
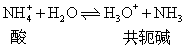
酸与碱既然是共轭的,它们的离解常数Ka与Kb之间必然有一定的联系。NH3-NH+4之间存在如下关系:

在其他的酸溶液或碱溶液中,同样可推算[H3O+][OH-] =Kw=1.0×10-14mol·L-2,因而不要误认为酸溶液中没有OH-或碱溶液中没钉H+。