两条异面直线的公垂线liangtiao yimian zhixiande gongchuixian
与两条异面直线都垂直相交的直线.
可以证明:两条异面直线有且只有一条公垂线.
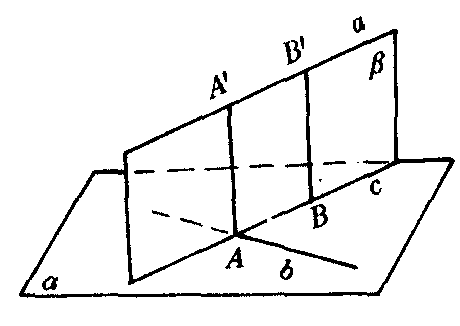
图1
如图1,设a,b是异面直线.过b作平面α,使α∥a.过a作平面β,使β⊥α.设α∩β=c.则a∥c.因此c,b相交.设b∩c=A.在β内过A作c的垂线与a交于A′.因为β⊥α,所以AA′ ⊥α.又b⊂α,所以AA′⊥b.因为a∥c,所以AA′⊥a.又因为AA′∩a=A′,AA′∩b=A,所以AA′是a,b的公垂线.这说明两条异面直线有公垂线.
下面证明两条异面直线的公垂线是唯一的.
假设BB′为异面直线a,b的另一条公垂线.因为BB′⊥a,所以BB′⊥c.因为BB′⊥b,所以BB′⊥α.又因为AA′⊥α,所以AA′∥BB′.因此A,A′,B,B′共面.即a,b共面.与已知条件a,b是异面直线矛盾,所以AA′是a,b唯一的一条公垂线.
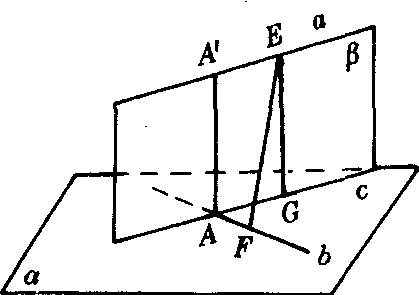
上述结果说明,我们用异面直线的公垂线段的长来定义异面直线的距离是合理的.同时,我们还可以证明AA′的长是分别在a,b上两点间的距离中最小的. 如图2,设在a,b上分别取点E和F.连结EF.在平面β内过点E作c的垂线EG,垂足为G.则EG⊥a.因此EG
图2
通过上面的证明,还可以看出:异面直线a,b的距离,也就是a和过b且平行于a的平面a间的距离.利用这一性质可以求两条异面直线的距离(参见“两条异面直线的距离”).