百分数和分数的互化Baifenshu he fenshu de huhua
百分数可以看作分母是100的分数,所以百分数与分数、小数可以进行互化。
百分数化成分数的方法是去掉百分号, 把所得数作分子,用100作分母,然后把所得的分数化为最简分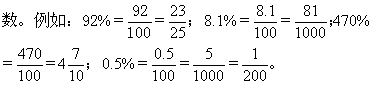
分数化成百分数的方法是先把分数化成小数 (遇到除不尽时,可按给定的精确度取近似值,一般要求保
- 三、人民公社时期的农村基层政权
- 三、人民公社时期的农村基层政权建设
- 三、人民公社时期的收益分配
- 三、人民公社的收益分配
- 三、人民公社的整顿
- 三、人民公社经济收益分配
- 三、以市场为导向兴办农工商联合企业
- 三、以市场需求为导向,建立商品基地,大搞农业综合开发
- 三、以点带面,提高果业规模经营效益
- 三、企业、产业、产品结构
- 三、企业集团主要类型
- 三、伊犁、博尔塔拉旅游区
- 三、伊犁哈萨克自治州
- 三、伊犁河谷农牧林区
- 三、优待抚恤
- 三、优待抚恤与复员退伍军人安置
- 三、优待抚恤工作
- 三、优抚安置
- 三、优良作物和畜禽品种的交换
- 三、传染病与地方病防治
- 三、体制调整
- 三、体坛名将
- 三、作物和畜禽品种的交流和引进
- 三、作物良种重要项目的开发推广
- 三、佳木斯市