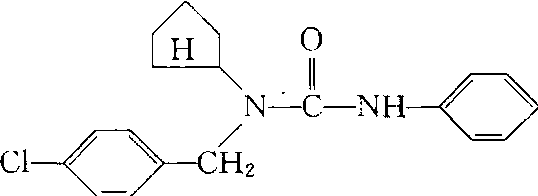
禾穗宁Pencycuron
又名戊菌隆、万菌灵。取代脲类杀菌剂。化学名称:1-(4-氯苯基)-1-环戊基-3-苯基脲。化学结构式如下。原药无色结晶,20℃时在100g溶剂中水中溶解度为0.00005 g,甲醇1~5g,丙酮10~20g,氯仿20~40g,甲苯1~5g,二甲基甲酰胺760 g。由日本特殊农药公司研制。选择性杀菌剂,主要对丝核菌引起的病害有特效,抑制菌核萌芽和菌丝生长。对水稻纹枯病具有保护和治疗作用,残效期15~20天。可叶面喷洒,亦可土壤处理,防治苗期立枯病,对植物安全。对大鼠急性口服LD50>5 000mg/kg,经皮LD50>5 000 mg/kg,对皮肤、眼睛无刺激作用,无致畸,致突变作用。