竹䇲鱼horse mackerel
硬骨鱼纲,鲈形目,鲹科,竹䇲鱼属(Trachurus)鱼类的通称。体纺锤形,侧扁。眼大,脂眼睑发达。口大,前位,口裂倾斜。前颌骨能伸缩。上颌骨后端伸达眼前缘稍后下方。上下颌各具一行细牙,犁骨、腭骨及舌面均具牙。体被小圆鳞,侧线上全部被高而强的棱鳞,在尾柄处形成一隆起嵴。背鳍和臀鳍后方无小鳍。为中上层暖温性鱼类。种类甚多,世界上产量较大的有智利竹䇲鱼(T.murphyi)分布于东太平洋的中部及南部,年产250万~280万t,居世界主要经济鱼类的第3至第5位。南非竹䇲鱼(T.capensis)分布于东南大西洋,年产50万~60万t。 日本竹䇲鱼(T.japonicus),亦称黄,长约40 cm。背部青黄绿色。游泳迅速,喜结群,对声音感觉灵敏。白天栖息较深水层,夜晚有趋光习性,灯光可将它诱集到表层。生殖季节游向近岸,天气晴朗时成群上浮。春季产卵,卵浮性。摄食桡足类、虾、蟹和鲱科及鳀科幼鱼。分布于朝鲜、日本和中国沿海。年产20万~30万t,是中国灯光围网作业对象之一,常见的经济鱼类。肉质佳,多制成盐干品,部分鲜销或制罐。
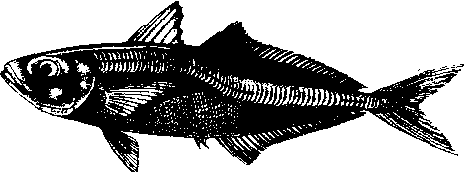
竹䇲鱼
- 坚持人民民主专政,反对用资产阶级人权搞动乱
- 坚持以经济建设为中心,坚持党的基本路线毫不动摇
- 坚持党对干部的管理
- 坚持党的基本路线一百年不动摇
- 坚持公有制为主体多种经济成分并存
- 坚持共产主义理想
- 坚持农、职业中学教育改革,办出了地方特色
- 坚持凭政绩选人用人
- 坚持和改善党的领导
- 坚持四项基本原则
- 坚持四项基本原则学习手册
- 坚持四项基本原则教育
- 坚持四项基本原则是社会主义法制建设的根本前提
- 坚持性
- 坚持改革开放
- 坚持改革开放的方针
- 坚持无产阶级专政
- 坚持每天热水洗脚
- 坚持沂蒙山区
- 坚持独立自主的和平外交政策
- 坚持用四项基本原则教育人民
- 坚持社会主义道路
- 坚持科教兴市战略加快科技产业化的实施意见
- 坚持适中
- 坚持马克思列宁主义、毛泽东思想