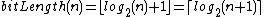- See also
- References
Bit-length or bit width is the number of binary digits, called bits, necessary to represent an integer[1] in the binary number system. Formally the number of bits of zero is 1 and any other natural number  is a function, bitLength(n), of the binary logarithm of n:
is a function, bitLength(n), of the binary logarithm of n:
At their most fundamental level, digital computers and telecommunications devices (as opposed to analog devices) can process only data that has been expressed in binary format. The binary format expresses data as an arbitrary length series of values with one of two choices: Yes/No, 1/0, True/False, etc., all of which can be expressed electronically as On/Off. For information technology applications, the amount of information being processed is an important design consideration. The term bit-length is technical shorthand for this measure.
For example, computer processors are often designed to process data grouped into words of a given length of bits (8 bit, 16 bit, 32 bit, 64 bit, etc.). The bit-length of each word defines, for one thing, how many memory locations can be independently addressed by the processor. In public-key cryptography, keys are defined by their length expressed in binary digits - their bit length.
See also
- Bit width
References
- Galo Plaza
- Galo Plaza Lasso
- Galor class starship
- Galore (The Cure album)
- Galoshes
- GALP
- GAL (paramilitary group)
- Galrevkom
- Gals!
- Gals Panic
- Galston
- Galston, East Ayrshire
- Galston, New South Wales
- Galswintha
- Galswinthe
- Galsworthy
- Galsworthy, John
- Galt
- Galt, CA
- Galt, California
- Galt-Cayley Tariff
- Galtee Mountains
- Galten, Denmark
- Galten Municipality
- Galterius