到内映射daonei yingshe
设A,B是两个集合,如果f是从A到B的映射,且f的值域ℛ(f)是B的真子集,即ℛ(f) ⊂B,那么就称f是A到B内的映射(如图).
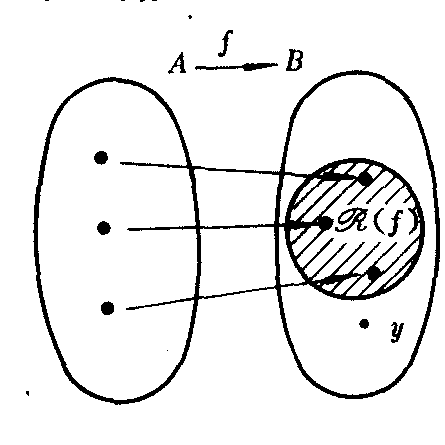
此时,B中将存在这样的元素y,它在A中没有原象.
| 词条 | 到内映射 |
| 类别 | 中文百科知识 |
| 释义 | 到内映射daonei yingshe设A,B是两个集合,如果f是从A到B的映射,且f的值域ℛ(f)是B的真子集,即ℛ(f) ⊂B,那么就称f是A到B内的映射(如图).
此时,B中将存在这样的元素y,它在A中没有原象. |
| 随便看 |
开放百科全书收录579518条英语、德语、日语等多语种百科知识,基本涵盖了大多数领域的百科知识,是一部内容自由、开放的电子版国际百科全书。