- Assessment
- Outliers, leverage and influence
- See also
- References
- Further reading
In statistics, an influential observation is an observation for a statistical calculation whose deletion from the dataset would noticeably change the result of the calculation.[1] In particular, in regression analysis an influential point is one whose deletion has a large effect on the parameter estimates.[2]
Assessment
Various methods have been proposed for measuring influence.[2][3] Assume an estimated regression  , where
, where  is an n×1 column vector for the response variable,
is an n×1 column vector for the response variable,  is the n×k design matrix of explanatory variables (including a constant),
is the n×k design matrix of explanatory variables (including a constant),  is the n×1 residual vector, and
is the n×1 residual vector, and  is a k×1 vector of estimates of some population parameter
is a k×1 vector of estimates of some population parameter  . Also define
. Also define  , the projection matrix of
, the projection matrix of  . Then we have the following measures of influence:
. Then we have the following measures of influence:
-
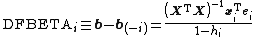 , where
, where  denotes the coefficients estimated with the i-th row
denotes the coefficients estimated with the i-th row  of
of  deleted,
deleted,  denotes the i-th row of
denotes the i-th row of  . Thus DFBETA measures the difference in each parameter estimate with and without the influential point. There is a DFBETA for each point and each observation (if there are N points and k variables there are N·k DFBETAs).&91;4&93;
. Thus DFBETA measures the difference in each parameter estimate with and without the influential point. There is a DFBETA for each point and each observation (if there are N points and k variables there are N·k DFBETAs).&91;4&93; - DFFITS
- Cook's D measures the effect of removing a data point on all the parameters combined.&91;5&93;
Outliers, leverage and influence
An outlier may be defined as a surprising data point. Leverage is a measure of how much the estimated value of the dependent variable changes when the point is removed. There is one value of leverage for each data point.[6] Data points with high leverage force the regression line to be close to the point.[5] In Anscombe's quartet, only the bottom right image has a point with high leverage.
See also
- Outlier
- Leverage
- Partial leverage
- Regression analysis
- {{slink|Cook's distance|Detecting highly influential observations}}
- Anomaly detection
References
2. ^{{cite web |first=Larry |last=Winner |title=Influence Statistics, Outliers, and Collinearity Diagnostics |work= |date=March 25, 2002 |url=http://stat.ufl.edu/~winner/sta6127/influence.doc }}
3. ^{{cite book |last=Belsley |first=David A. |last2=Kuh |first2=Edwin |last3=Welsh |first3=Roy E. | year=1980 |title=Regression Diagnostics: Identifying Influential Data and Sources of Collinearity |publisher=John Wiley & Sons |location=New York |series=Wiley Series in Probability and Mathematical Statistics |isbn=0-471-05856-4 |pages=11–16 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=GECBEUJVNe0C&pg=PA11 }}
4. ^{{cite web |title=Outliers and DFBETA |url=http://www.albany.edu/faculty/kretheme/PAD705/SupportMat/DFBETA.pdf |dead-url=no |archivedate=May 11, 2013 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20130511013229/http://www.albany.edu/faculty/kretheme/PAD705/SupportMat/DFBETA.pdf }}
5. ^1 2 {{cite book | last = Everitt | first = Brian | title = The Cambridge Dictionary of Statistics | publisher = Cambridge University Press | location = Cambridge, UK New York | year = 1998 | isbn = 0-521-59346-8 }}
6. ^{{cite web |first=Clifford |last=Hurvich |title=Simple Linear Regression VI: Leverage and Influence |publisher=NYU Stern |url=http://pages.stern.nyu.edu/~churvich/Undergrad/Handouts2/31-Reg6.pdf |dead-url=no |archivedate=September 21, 2006 |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20060921160749/http://pages.stern.nyu.edu/~churvich/Undergrad/Handouts2/31-Reg6.pdf }}
Further reading
- {{cite journal |first=Catherine |last=Dehon |first2=Marjorie |last2=Gassner |first3=Vincenzo |last3=Verardi |title=Beware of ‘Good’ Outliers and Overoptimistic Conclusions |journal=Oxford Bulletin of Economics and Statistics |volume=71 |issue=3 |pages=437–452 |year=2009 |doi=10.1111/j.1468-0084.2009.00543.x }}
- {{cite book |first=Peter |last=Kennedy |authorlink=Peter Kennedy (economist) |chapter=Robust Estimation |title=A Guide to Econometrics |location=Cambridge |publisher=The MIT Press |edition=Fifth |year=2003 |isbn=0-262-61183-X |pages=372–388 |chapterurl=https://books.google.com/books?id=B8I5SP69e4kC&pg=PA372 }}