流域平均高度
流域地表的平均高程。其计算方法是在流域地形图上,用求积仪分别量取相邻等高线间的面积,然后按下列公式进行计算:
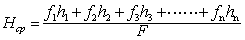
f1 f2 f3 fn——相邻两等高线间的面积(平方公里)
h1 h2 h3 hn——相邻两等高线间的平均高程(米)
F——流域总面积(平方公里)
Hcp——流域平均高度(米)
流域平均高度直接影响流域的气温、降水和蒸发。
| 词条 | 流域平均高度 |
| 类别 | 中文百科知识 |
| 释义 | 流域平均高度流域地表的平均高程。其计算方法是在流域地形图上,用求积仪分别量取相邻等高线间的面积,然后按下列公式进行计算:
f1 f2 f3 fn——相邻两等高线间的面积(平方公里) h1 h2 h3 hn——相邻两等高线间的平均高程(米) F——流域总面积(平方公里) Hcp——流域平均高度(米) 流域平均高度直接影响流域的气温、降水和蒸发。 |
| 随便看 |
开放百科全书收录579518条英语、德语、日语等多语种百科知识,基本涵盖了大多数领域的百科知识,是一部内容自由、开放的电子版国际百科全书。