三氧化硫sanyanghualiu
S (Ⅵ) 的氧化物,主要以两种状态存在,化学式分别表示为SO3或(SO3) n,又称硫酸酐。通常为无色有刺激味的气体,以单体SO3形式存在。分子呈平面三角形,它与BF3,NO-3及CO2-3等为等电子体。中心硫 子使用sp2杂化与氧原子的2p轨道构成σ键,S—O单键的键长约为155pm,而三氧化硫中的S—O键键长较短 (143pm),具有双键的性质,硫原子上垂直于平面的空p轨道,与氧原子相平行的p轨道形成大π键π64。三氧化硫蒸气在45℃时凝结,生成易挥发的液体,是单体与三聚体的混合物。当冷却至17℃时则凝成无色透明的冰状固体,固态三氧化硫有α-SO3,β-SO3和γ-SO33种变体。冰状变体由三聚分子(SO3)3形成。由于sp3杂化是硫的最大特征,故三氧化硫分子易聚合成环。环内S—O键为单键 (键长160pm),环外S—O键键长较短 (140pm),具有双键性质,在保存期间,冰状的三氧化硫渐渐转变为纤维状的三氧化硫 (这种结构要在痕量水存在下才能形成)。它是由许多SO-2基团通过氧原子互相连结起来的锯齿长链(SO3)n,纤维状变体在挥发性及与水的反应的活泼性方面都较冰状变体为小。
三氧化硫具有强氧化性,可使磷燃烧,使碘化物氧化为碘单质:
10SO3+4P=P4O10+10SO2
2KI+SO3=K2SO3+I2
三氧化硫溶于水得硫酸,工业上生产浓硫酸是用硫酸溶解三氧化硫,因其与水直接反应产生酸雾难以凝结。虽然从热力学角度看气态二氧化硫与氧气转化成三氧化硫是有利的 (
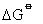 为-80.54kJ·mol-1),但反应速度小,要在催化剂 (五氧化二钒或铂) 的存在下,加热至400℃才能制得。三氧化硫主要用于制硫酸和氯磺酸,也用于有机化合物的磺化等方面。
为-80.54kJ·mol-1),但反应速度小,要在催化剂 (五氧化二钒或铂) 的存在下,加热至400℃才能制得。三氧化硫主要用于制硫酸和氯磺酸,也用于有机化合物的磺化等方面。