- Statement of theorem
- References
In convex analysis, the Fenchel–Moreau theorem (named after Werner Fenchel and Jean Jacques Moreau) or Fenchel biconjugation theorem (or just biconjugation theorem) is a theorem which gives necessary and sufficient conditions for a function to be equal to its biconjugate. This is in contrast to the general property that for any function 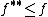 .[1][2] This can be seen as a generalization of the bipolar theorem.[1] It is used in duality theory to prove strong duality (via the perturbation function).
.[1][2] This can be seen as a generalization of the bipolar theorem.[1] It is used in duality theory to prove strong duality (via the perturbation function).
Statement of theorem
Let  be a Hausdorff locally convex space, for any extended real valued function
be a Hausdorff locally convex space, for any extended real valued function 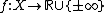 it follows that
it follows that 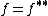 if and only if one of the following is true
if and only if one of the following is true
-
 is a proper, lower semi-continuous, and convex function,
is a proper, lower semi-continuous, and convex function, -
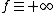 , or
, or -
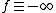 .&91;1&93;&91;3&93;&91;4&93;
.&91;1&93;&91;3&93;&91;4&93;
References
1. ^1 2 {{cite book |last1=Borwein |first1=Jonathan |authorlink1=Jonathan Borwein|last2=Lewis |first2=Adrian |title=Convex Analysis and Nonlinear Optimization: Theory and Examples| edition=2 |year=2006 |publisher=Springer |isbn=9780387295701|pages=76–77}}
2. ^{{cite book |last=Zălinescu |first=Constantin |title=Convex analysis in general vector spaces |publisher=World Scientific Publishing Co., Inc. |isbn=981-238-067-1 |mr=1921556 |issue=J |year=2002 |location=River Edge, NJ |pages=75–79}}
3. ^{{cite journal | author = Hang-Chin Lai | author2 = Lai-Jui Lin | date=May 1988 | title = The Fenchel-Moreau Theorem for Set Functions | journal = Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society | publisher = American Mathematical Society | volume = 103 | issue = 1 | pages = 85–90 | doi = 10.2307/2047532 | url = | format = | accessdate = }}
4. ^{{cite journal|title=A generalization of the Fenchel–Moreau theorem|author=Shozo Koshi|author2=Naoto Komuro|journal=Proc. Japan Acad. Ser. A Math. Sci.|volume=59|issue=5|year=1983|pages=178–181}}
{{DEFAULTSORT:Fenchel-Moreau theorem}}2. ^{{cite book |last=Zălinescu |first=Constantin |title=Convex analysis in general vector spaces |publisher=World Scientific Publishing Co., Inc. |isbn=981-238-067-1 |mr=1921556 |issue=J |year=2002 |location=River Edge, NJ |pages=75–79}}
3. ^{{cite journal | author = Hang-Chin Lai | author2 = Lai-Jui Lin | date=May 1988 | title = The Fenchel-Moreau Theorem for Set Functions | journal = Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society | publisher = American Mathematical Society | volume = 103 | issue = 1 | pages = 85–90 | doi = 10.2307/2047532 | url = | format = | accessdate = }}
4. ^{{cite journal|title=A generalization of the Fenchel–Moreau theorem|author=Shozo Koshi|author2=Naoto Komuro|journal=Proc. Japan Acad. Ser. A Math. Sci.|volume=59|issue=5|year=1983|pages=178–181}}
2 : Convex analysis|Theorems in analysis
- Ian Gilmour, Baron Gilmour of Craigmillar
- Ian Gilroy
- Ian Goldberg
- Ian Gow
- Ian Graham Davidson
- Ian Gregson
- Ian Grojnowski
- Ian Grushka
- Ian Hacking
- Ian Hamilton (advocate)
- Ian Hamilton (British Army officer)
- Ian Hamilton Finlay
- Ian Hamilton (footballer, born 1950)
- Ian Hancock
- Ian Hanomansing
- Ian Hargreaves
- Ian Hart
- Ian Harvey
- Ian Haugland
- Ian Healy
- Ian Hedworth John Little Gilmour
- Ian Henderson (police officer)
- Ian Hetherington
- Ian Hill
- Ian Hislop